Label Printers Overview
Have you ever wondered what it takes to make those labels that are everywhere, from the water bottles in your fridge to the shampoo bottle in your shower? Nowadays, all it takes is a label printer, and they’re becoming increasingly popular as they offer an easy and affordable way to neatly and professionally label items. But how exactly do these label printers work? In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how modern label printers operate and how they’re used in a variety of industries. From creating barcodes to writing name tags, you’ll know exactly how to make the most out of your label printer. So, let’s get started and explore the wonders of the modern label printer!
Label printers like the best WiFi printer, are an essential tool for any company, from large corporations to small home-based businesses. They provide an efficient way to produce labels and other printed material with precision and accuracy that would be difficult or impossible to produce by hand. But what exactly are label printers? How do they work? Let’s take a closer look at the basics of label printing.
Label printers come in a variety of shapes, sizes and styles, all designed to fulfill different needs. While technology has advanced considerably in recent years, label printing follows a basic pattern: data is received from a PC or other input source, processed through software such as Adobe Illustrator or Microsoft Word, and then sent to the printer itself. The printer then converts that data into a precise physical output.
The main debate surrounding label printers is the question of whether digital or traditional analog label printing is better for producing high-quality results. On one hand, digital printing allows users to customize their labels in faster turnaround times; however, analog printing can be more reliable for producing consistent results on different types of materials. Ultimately, it depends on how precise the user wants their labels to be and what materials are being used for the job.
Label printers offer a great opportunity for businesses of any size to reduce costs while maintaining excellent quality control standards. Now that we’ve taken a look at the overall process of label printing, let’s move on to discuss the various types of printers available today which can help meet your business needs even more effectively.
Types of Label Printers

Label printers come in various shapes and sizes, offering businesses a wide variety of options when selecting the best printer for their needs. There are three main types of label printers: inkjet, thermal transfer, and direct thermal. Each type has its own characteristics that make it the most suitable for certain types of labels.
Inkjet label printers are used to create printed images with great detail and accuracy. These printers use tiny jets of paint to produce labels at high resolution and precision on a variety of surfaces, including paper, plastic, cardstock, synthetics and fabrics. Thanks to its fast printing speed and wide range of colour gamut, an inkjet label printer is an excellent option for producing bright and vibrant labels with intricate designs or detailed fonts.
Thermal transfer label printers are ideal for businesses that need to print bulk labels quickly. This type of printer uses heat to transfer a coloured ribbon onto the desired materials such as paper, films, synthetics and some fabrics. Thermal transfer printers don’t require pricey ink refills, but they also lack the intricate level of detail found in inkjet printing.
Direct thermal label printers offer businesses a cost-effective solution for printing high-volume barcode labels and tags quickly. While it does require pricey dye ribbons like thermal transfer does, this type of printer can provide excellent value for money due to its fast printing speeds up to five inches per second. Direct thermal prints attributes such as smearing or fading when exposed to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight; therefore, it is not suitable for long-term storage applications where higher durability is required.
With so many different types of label printers available on the market today, deciding which one will best suit your business needs can be quite a challenge. Fortunately, there are specialists who can help you in choosing the right device depending on your unique requirements. Now that you know the basics about each type of label printer, let us now take a closer look at how an inkjet label printer works.
How Does an Inkjet Label Printer Work?

An inkjet label printer is a popular choice among consumers because it yields high-quality labels with detailed graphics and text. An inkjet label printer works by using tiny nozzles that spray micron-sized droplets of liquid ink onto the surface of the label. The size and amount of droplets released are controlled by software, so users can adjust their settings to get the desired look for their labels. Inkjet printers also provide more vibrant color and sharper results than other types of printing methods. This makes them ideal for high-end labels or custom designs that require great detail.
On the downside, inkjet printers can be expensive and use more ink than other types of printers which means higher long-term costs. Additionally, the drying time for each label can be lengthy due to the nature of the ink used in these printers. However, when you need premium quality labels, an inkjet printer is often difficult to beat.
Overall, while they may not be quite as cost effective as thermal and dot matrix printers, if you’re looking for lasting labels with detailed designs, an inkjet printer could be your best option. Thanks to advancements in technology, there are many models on the market today offering top-notch quality without breaking your budget. So now that you know how an inkjet label printer works, let’s explore more about the components and principles underlying normal label printing operations.
Components and Principles
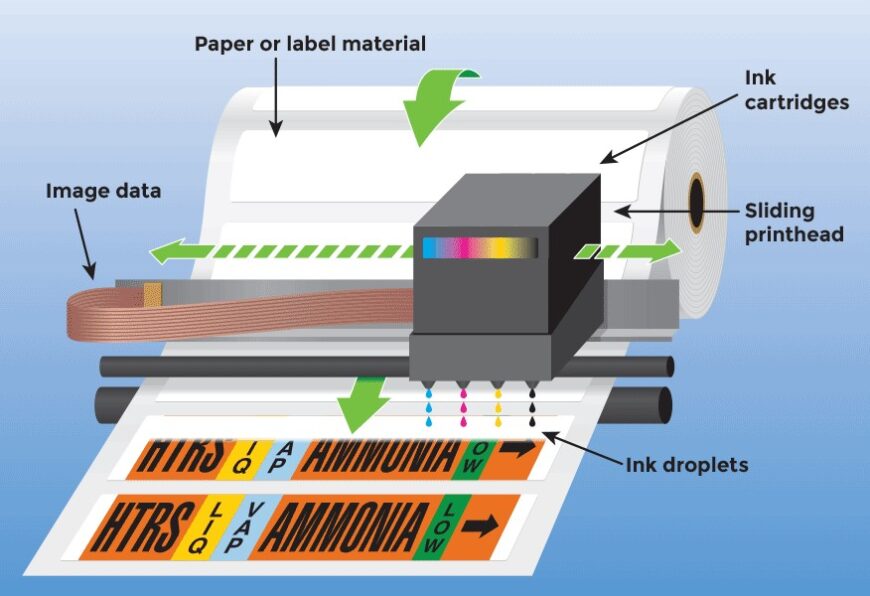
When discussing the components and principles of label printers, it is important to note the differences between inkjet and laser designs. Inkjet label printers work by ejecting tiny droplets of liquid ink that are directed onto the surface at high speeds to form an image or text on a printed label. Since they deposit ink in small amounts, they not only produce high resolution images but also save on ink consumption. On the other hand, laser label printers utilize toner cartridges instead of ink cartridges and use heat to transfer toner particles onto the printing surface in order to produce darker lines with thicker edges. This makes them capable of printing high-contrast images with greater durability than inkjet prints.
The most important element in any printer regardless of technology type is its components – these directly impact its printing quality, consumption rate and reliability. Common components for inkjet and laser printers include print heads (or imaging drums), media retainers, sensors, feeders and print belts. Each part works together to create an output depending on how it is programmed and manipulated by a controller unit. While both technologies operate differently, the basic principles such as printing resolution and speed are essentially the same since each has to depend on mechanisms like feed speed, head movement speed and number of nozzles for making decisions about quality and quantity.
Before transitioning to the next section, it is worthwhile to consider which type of label printer is right for you. Inkjet printers are typically cheaper, more reliable and easier to manage but may consume more ink over time; while laser printers can handle larger volumes with greater overall accuracy albeit at higher maintenance cost.
Now that we have discussed the components and principles associated with label printers, let’s move on to examining another technology type – one that uses light beams instead of liquid or powder-based solutions – and see how it works in practice.
How Does a Laser Label Printer Work?

Label printers are fascinating pieces of technology, and their components and principles can be just as captivating. Oftentimes, a label printer combines several key elements to create advanced printing. Of course, the type of printer used will determine which specific components are used: laser or inkjet.
Starting with laser label printers, it’s possible to directly transfer text and images onto labels through the use of lasers. This technology works by utilizing a rotating drum and a laser beam along with charged particles. The process creates an electrical charge that causes the colors on the label to become visible. Laser label printers typically allow for more intricate designs with sharper details while being more effective in conserving toner than other methods. With this method, precise control of colors is possible thanks to fuser oils and heat temperatures that melt the toner onto the paper.
On the other hand, many inkjet label printers utilize liquid inks for each color layer of the printout. Inkjet technology works by using droplets of ink that are sprayed onto the surface of the paper. Unlike laser printers, inkjet models don’t require toner cartridges in order to produce labels — instead, they make use of water-soluble pigments such as dyes or sublimation inks. The advantage is that these printers don’t require warm-up time, nor do they have any toxic emissions like those produced by laser models. They also tend to be far more affordable compared to lasers when it comes to purchasing them outright.
As you can see, depending on which type of printer you choose, you can get a whole range of component parts and principles. But now let’s delve into the field even further and examine some of the more advanced technologies available today in label printers.
Components and Principles
Various types of label printers exist, each designed in its own way to suit the needs of their customers. One type specifically is a laser label printer, which utilizes laser technology to print sharp and precise labels and documents. How, exactly, does a laser label printer work?
The basic operation of a laser label printer is similar to that of a traditional monochrome laser printer. It begins with creating an electric charge on an imaging drum using light from a semiconductor source, which creates an electrostatic latent image on the imaging drum. Then, this image is developed on to the imaging drum by an electrically charged toner, which has been heated and melted on contact with the latent image. The toner then binds to the paper leaving it with a permanent transfer of data printed onto it.
One major feature in a laser label printer is that it prints edge-to-edge selections rather than margins from both sides of the document. This results in labels appearing crispier with less blurring or smudging around stains caused due to faint sketches or drawings. In addition to that, printing times for these lasers are typically faster than other printers since there’s no need for setting margins or waiting for pitch adjustments with the laser technology therefore ensuring more efficient process management when it comes to mass printing jobs.
Generally speaking, laser label printers reliably produce satisfactory results that offer users ample flexibility in getting creative with their labels while being highly economical compared to other systems available on the market today. As such, they have become essential tools for any business aiming for higher efficiency and productivity in labeling tasks.
Though modern laser label printers can work wonders when it comes to producing excellence in precision and accuracy right away without any additional processing, this doesn’t come without its challenges as well – namely high energy consumption and frequent maintenance requirements due to their complex inner workings which require expertise. Having said that, they still remain significantly popular among those who look for a productive solution in labeling tasks.
With all this in mind about how laser label printers work, it’s important to consider what components these machines contain so we can better understand how they operate from within – something we’ll now move on to discussing next.
Advanced Label Printer Technology

In terms of label printer technology, one of the more advanced concepts is thermal transfer printing. This method is a hybrid technology; combining elements of both direct thermal printing and thermal transfer printing. First, a printhead heats up a special ribbon that contains colored plastic, wax, or resin material. This then thermally dyes the material onto the backing of the label stock thus creating imagery. Due to its hybrid nature, thermal transfer offers advantages over direct thermal for certain applications such as those requiring resistance to light and heat or durability in harsh or outdoor environments.
The most specialized and latest innovations are digital label printers, using either inkjet or laser technologies to create labels. With digital printing solutions comes extraordinary color options, personalizations and barcode capabilities that are not easily attainable with other technologies. Compared to traditional methods of flexing/screen printing and hot stamping/letter press printing, which require costly investment in equipment and supplies, digital labeling offers much lower start-up costs. In addition, because no plates or cylinders are necessary for setting up a job, it can be done faster since images can be changed quickly and new ones added with little effort.
At this level of technology we have many elements to consider: ease of setup and use; media flexibility; color accuracy; short run capability; speed; networking capability; environment requirements and resource usage (ink, toner). These considerations should all be carefully weighed when buying to get the best performance out of your system. To help best compare modern requirements and options between products it may be wise to seek guidance from an expert provider who can work with you in making the best choice for your specific needs. As you make your selection remember that close comparison between inkjet and laser label printers is essential in order to find the right match for what you need now and in the future.
Comparisons Between Inkjet and Laser Label Printers

It is important to consider the differences between inkjet and laser label printers when selecting which type of printer to use. Inkjet label printers utilize a system of nozzles that spray droplets of ink onto the paper or media, resulting in a high-quality output potential. This type of printer is ideal for printing on demand as its print head rapidly moves across the page. It also requires no special processes, allowing for a quick and convenient color printing experience with multiple media types.
On the other hand, laser label printers are more efficient and cost-effective in terms of toner usage compared to inkjet devices. The primary benefit of laser printing is speed; many models can produce up to 12 pages per minute and an entire page can be printed out in mere seconds. Additionally, the superior resolution of laser technology produces clean graphics, deep blacks, and sharp text – all at a fraction of the cost when compared to inkjet models.
Inkjet label printers provide better colors due to the large assortment of available media types. In addition, the paper is immersed in ink which helps prevent running of colors after printing. Laser label printers are renowned for their longevity and their ability to create incredibly detailed images without smudging or fading over time. Laser toners also dry quickly after printing, decreasing production time significantly when working with larger batches.
Ultimately it comes down to individual preference – while there are pros and cons to each option, it is essential that users select a printer that meets their specific needs rather than relying on one choice as a universal solution. If convenience is paramount then an inkjet option may be preferable albeit slightly pricier due to replacement cartridges costs; in contrast laser models offer a much longer shelf life so they may be more economical in terms of total use over time.
Frequently Asked Questions and Responses
What are the advantages of using a label printer?

The advantages of using a label printer are numerous. First, label printers enable the creation of custom labels that can be tailored to any need. From names, logos, addresses and instructions to more complex designs like barcodes or QR codes, users can create exactly what they need. Second, label printers save time and money over traditional printing methods. The low cost of consumables such as ink cartridges and labels combined with their fast printing speed make them extremely cost-effective for businesses. Finally, label printers offer high levels of accuracy, producing consistent results with minimal errors, making them ideal for any number of applications.
How do different types of labels affect the printing process?
The type of labels used in a printing process will affect the quality of the final product. Different types of labels use different adhesives and materials, which can lead to differences in printing results. For example, paper or plastic labels require different adjust settings on the printer that correspond to their material. Thermal labels are particularly sensitive – using the wrong kind of thermal paper may result in no adhesive doing its job, leading to zero stickiness for the label. Choosing the right label and adjusting settings accordingly is key for achieving printing success.
What types of label printers are available?
Label printers come in a variety of shapes, sizes and capabilities, ranging from desktop models perfect for small-scale businesses or home offices to industrial models designed for large-scale operations. Popular types of label printers include:
• Thermal Transfer Printers: This type of printer uses a ribbon and thermal technology to print onto a wide range of materials like paper, film and synthetics. Thermal transfer printers are often used in industrial settings as they provide accurate, consistent and reliable results.
• Direct Thermal Printers: Unlike thermal transfer printers, direct thermal printers don’t require ribbons. Instead, these printers create images using thermally sensitized paper. This makes them ideal for on-demand tasks and low-volume printing applications due to their fast printing capabilities.
• Inkjet Printers: Inkjet printers use liquid ink to create high-resolution prints on various materials including paper, plastic and fabric. Depending on the model, inkjet label printers offer excellent speed and versatility.
• Laser Printers: Laser printers use a laser beam to create an image on specially treated paper or other materials. Similar to inkjet printers, laser printers are great for producing labels with sharp text and images at a relatively fast speed.
No matter which type of label printer you choose, it’s important to make sure that it meets the specific requirements of your business or personal needs so that you can get the best possible performance out of it.




