Mobile applications have become an integral part of our lives in this hyperconnected digital world. From online banking and entertainment to healthcare and shopping, nearly every activity now involves a mobile app. While this convenience is undeniable, it has also opened the door to an alarming rise in cyber threats. Malicious hackers are constantly searching for vulnerabilities to exploit and this makes app security more crucial than ever.
Businesses can no longer treat app protection as a secondary concern. Instead, it must be built into the core of the development process. To truly safeguard sensitive user data and ensure smooth user experiences, developers need to understand the multiple layers that make up modern app security.
1. The Foundation ─ Secure Coding Practices
The first and most essential layer of app security starts during development. Secure coding involves writing clean, efficient, and vulnerability-free code from the ground up. Developers must follow best practices such as input validation, code obfuscation, and minimizing hardcoded credentials.
Secure coding isn’t just about avoiding common mistakes; it’s about adopting a security-first mindset. For example, developers should always sanitize user inputs to prevent SQL injections or cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. They should also avoid using outdated libraries and ensure that encryption protocols are updated regularly.
By focusing on secure coding, developers build stronger foundations making it much harder for attackers to exploit weaknesses later on.
2. The Next Shield ─ Application Hardening
Once an app is developed, it’s time to fortify it against tampering and reverse engineering. This process, known as application hardening, protects the app from being modified or analyzed by unauthorized users.
Hardening involves several protective techniques, such as:
- Code obfuscation: Making the app’s source code difficult to read or interpret.
- Anti-tampering: Detecting and preventing unauthorized changes to the app’s code or files.
- Integrity verification: Ensuring that the app has not been altered since its last approved build.
These methods discourage hackers from decompiling or modifying apps to insert malicious code. It’s like locking all entry points before an intruder even gets a chance to try the door.
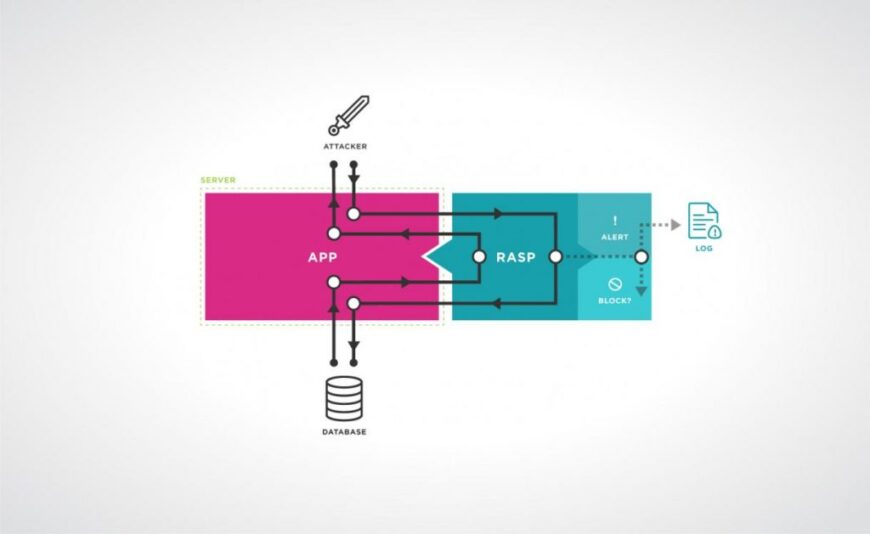
3. Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP)
Modern app security doesn’t stop once an app is deployed. During runtime when the app is actively being used, it’s exposed to potential attacks in real time. That’s where Runtime Application Self-Protection, or RASP, comes into play.
RASP solutions continuously monitor the app’s behavior while it runs. If they detect unusual or malicious activity, they can automatically block the threat or shut down the application before any damage occurs. For instance, if someone tries to inject malicious code or modify memory, RASP will identify the abnormal pattern and take immediate action.
This adaptive, self-defending mechanism makes RASP one of the most powerful tools in the modern security stack. It ensures protection even in hostile environments like rooted devices or unsecured networks where traditional security methods might fail.
4. Data Encryption and Secure Storage
Data is the heart of any mobile app and often its most valuable target. Encrypting sensitive information ensures that even if hackers manage to access it, the data remains unreadable.
Encryption should be applied to both data in transit (information moving between servers and devices) and data at rest (information stored within the device or app database).
Using robust algorithms like AES-256 or RSA adds a strong layer of defense. Moreover, sensitive credentials and tokens should never be stored in plain text. Instead, use secure storage options such as encrypted keychains or Android Keystore.
When encryption is implemented correctly, it minimizes the impact of breaches and strengthens the trust users place in the application.
5. Authentication and Access Control
Strong authentication systems are vital to ensuring that only authorized users can access the app. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) such as OTPs, biometric scans, or security questions provides an extra layer of protection beyond just a password.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is equally important for enterprise-level apps. It ensures that users only have access to the features or data relevant to their role. For example, an employee app might restrict certain administrative features to management-level users only.
This structured access prevents unauthorized operations and reduces internal risks, which are often overlooked in the broader app security framework.

6. API Security
Most modern apps rely heavily on APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for communication with servers or third-party services. However, APIs can become a weak point if not properly secured.
Developers must authenticate and authorize every API call, validate all data exchanged, and limit exposure of sensitive endpoints. Using API gateways, token-based authentication, and encryption helps strengthen the security of these connections.
Moreover, monitoring API traffic for anomalies ensures early detection of suspicious activities, such as repeated login attempts or abnormal data requests. Protecting APIs is vital because they often act as the bridge between user data and the app’s backend systems.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Modern cyberattacks are constantly evolving, and static defenses are no longer sufficient. Continuous monitoring and proactive threat intelligence have become key components of effective app security.
By tracking user behavior, network patterns, and potential vulnerabilities, security teams can detect unusual activities before they escalate. Integration of automated threat detection tools and analytics further enhances responsiveness.
Regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability scanning also ensure that the app remains resilient against emerging threats. Security, after all, is not a one-time task, it’s a continuous process of improvement and adaptation.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS impose strict standards for handling sensitive information. Compliance not only protects businesses from penalties but also builds user confidence.
Developers must ensure that the app meets all legal and privacy requirements relevant to its industry and region. Incorporating privacy-by-design principles ensures that data protection is integrated from the earliest stages of development.
Compliance also demonstrates a brand’s commitment to responsible digital practices, making it an essential component of holistic app security.

9. The Human Element
Even the most sophisticated security systems can fail if users and employees aren’t aware of best practices. Educating both developers and end-users about safe behaviors such as avoiding public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions or not downloading unverified apps adds another line of defense.
Conducting regular training sessions for development teams helps them stay updated on the latest attack vectors and prevention techniques. In the end, human awareness is often the first step toward preventing cyber incidents.
Conclusion
As digital threats continue to grow in complexity, businesses must adopt a layered and proactive approach to app security. Each layer from secure coding and encryption to runtime protection and continuous monitoring plays a vital role in shielding applications from evolving risks.
Security should no longer be seen as an add-on or afterthought. Instead, it’s a continuous journey that blends technology, strategy, and awareness. Companies that invest early in robust protection not only safeguard their data but also earn long-term user trust and credibility.









